This article’s code is basically from here. I will show Template Method pattern, which is one of the design patterns.
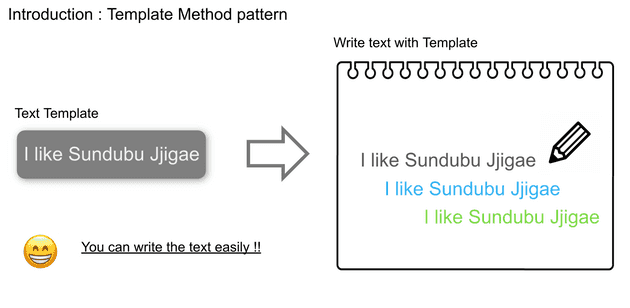
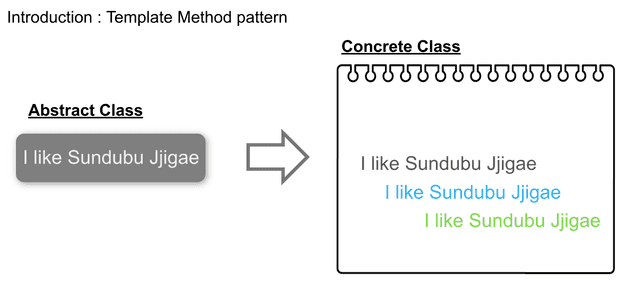
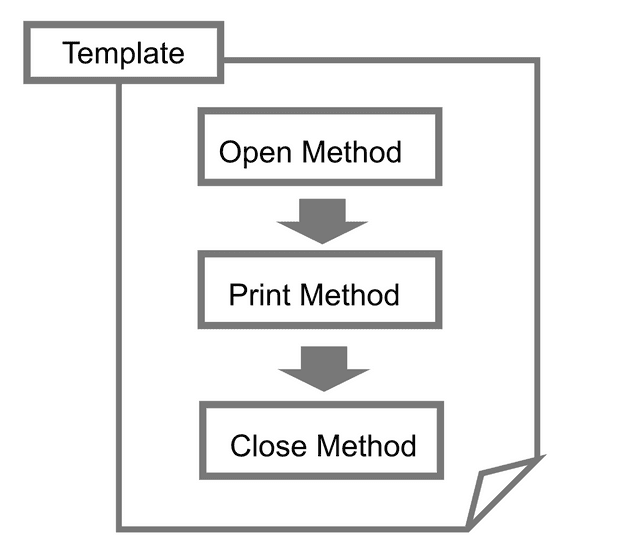
Abstract Class
public abstract class AbstractDisplay { // Abstract class
public abstract void open(); // abstract method1 open
public abstract void print(); // abstract method2 print
public abstract void close(); // abstract method3 close
public final void display() {
open(); // first, open
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { // print 5 times
print();
}
close(); // last, close
}
}
Main Class to utilize abstract and concrete class
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AbstractDisplay d1 = new CharDisplay('H');
AbstractDisplay d2 = new StringDisplay("Hello, world.");
d1.display();
d2.display();
}
}
Concrete Class Sample1 charDisplay
public class CharDisplay extends AbstractDisplay {
private char ch;
public CharDisplay(char ch) {
this.ch = ch;
}
public void open() {
System.out.print("<<");
}
public void print() {
System.out.print(ch);
}
public void close() {
System.out.println(">>");
}
}
Sample1 output
<<HHHHH>>Concrete Class Sample2 stringDisplay
public class StringDisplay extends AbstractDisplay {
private String string;
private int width;
public StringDisplay(String string) {
this.string = string;
this.width = string.getBytes().length;
}
public void open() {
printLine();
}
public void print() {
System.out.println("|" + string + "|");
}
public void close() {
printLine();
}
private void printLine() {
System.out.print("+");
for (int i = 0; i < width; i++) {
System.out.print("-");
}
System.out.println("+");
}
}
sample2 output
+---------------+
|Hello, world.|
|Hello, world.|
|Hello, world.|
|Hello, world.|
|Hello, world.|
+---------------+Pros
- Logic can be shared.
- We do not have to write same code.
- Easy to test / Less code to fix.
Cons
- Difficult to decide how much should be standardized and left to individual implementation
- If you don’t design to cover all the patterns that could be used, you will end up with a template that is difficult to apply.